 The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program is designed to stimulate the U.S. economy through job creation and capital investment by foreign investors. In exchange for making a minimum investment into a new U.S. business that results in the creation of at least 10 jobs, foreign investors may secure legal residency for themselves and their families.
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program is designed to stimulate the U.S. economy through job creation and capital investment by foreign investors. In exchange for making a minimum investment into a new U.S. business that results in the creation of at least 10 jobs, foreign investors may secure legal residency for themselves and their families.
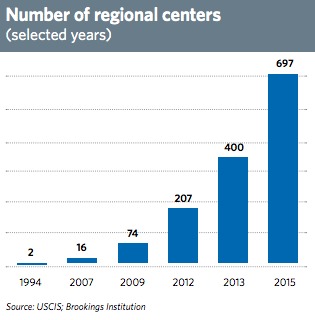
Typically, foreign investors find it advantageous to participate in the program by means of an authorized Regional Center—an economic entity (public or private) that promotes economic growth and job creation and adheres to the terms of the EB-5 Regional Center Pilot Program.
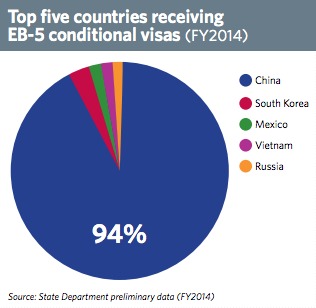
Since 2003, EB-5 Regional Centers have invested over $3.1 billion of foreign capital into the U.S. economy, creating over 65,000 jobs for U.S. workers. By stimulating the economy, the EB-5 program also stimulates real estate markets across the U.S.
Reauthorization
The EB-5 Regional Center Program was originally set to expire last September. Six distinct reauthorization bills were introduced in 2015, all attempting to usher in reforms that would make the program more transparent, accountable, and permanent.
In spite of intense negotiations with the EB-5 Investment Coalition (NAR is a member of this coalition) and other stakeholders, it became clear that the details of a complex and difficult EB-5 immigration reform bill could not be resolved prior to the deadline. Among the goals under review:
Fraud and security risks
Increase Regional Centers’ financial disclosure requirements and the use of background checks on Regional Center principals, participants and project developers.
Job creation
Eliminate certain ambiguities on job creation numbers.
National security
Ensure the vetting process for visa applicants is adequate.
At the last moment, the EB-5 Regional Center Pilot Program was extended until September 2016, giving the U.S. Congress more time to hammer out permanent reforms.
See NAR’s policies on immigration and other advocacy issues.












